
Inspector: Jim Keller
Inspector's phone: (906) 396-6706


Summary
| Client(s): | Sample Report 6 |
| Property address: | 1222 Any Rd Anytown, MI |
| Inspection date: | Wednesday, August 19, 2020 |
This report published on Thursday, October 22, 2020 4:07:31 PM CDT
This report is the exclusive property of this inspection company and the client(s) listed in the report title. Use of this report by any unauthorized persons is prohibited.
| Safety | Poses a risk of injury or death | |
| Repair/Replace | Recommend repairing or replacing | |
| Repair/Maintain | Recommend repair and/or maintenance | |
| Minor Defect | Correction likely involves only a minor expense | |
| Maintain | Recommend ongoing maintenance | |
| Evaluate | Recommend evaluation by a specialist | |
| Monitor | Recommend monitoring in the future | |
| Comment | For your information |
Grounds
2) 
 Handrails at deck stairs were missing. This is a potential fall hazard. Handrails should be installed at stairs with four or more risers or where stairs are greater than 30 inches high. Recommend that a qualified contractor install handrails where missing and per standard building practices.
Handrails at deck stairs were missing. This is a potential fall hazard. Handrails should be installed at stairs with four or more risers or where stairs are greater than 30 inches high. Recommend that a qualified contractor install handrails where missing and per standard building practices.
3) 
 Handrails at deck stairs were not graspable and posed a fall hazard. Handrails should be 1 1/4 - 2 inches in diameter if round, or 2 5/8 inches or less in width if flat. Recommend that a qualified person install graspable handrails or modify existing handrails per standard building practices.
Handrails at deck stairs were not graspable and posed a fall hazard. Handrails should be 1 1/4 - 2 inches in diameter if round, or 2 5/8 inches or less in width if flat. Recommend that a qualified person install graspable handrails or modify existing handrails per standard building practices.
4) 
 Perimeter bench seating was installed at one or more decks where walking surfaces were more than 30 inches above the surrounding grade. Bench seating is not a safe substitute for standard guardrails, and is a potential fall hazard. Gaps in such seating often allow small children to climb underneath and fall. People sitting or standing on benches may also fall. The clients should at least be aware of this hazard, especially if small children are present. Recommend having a qualified contractor repair as necessary to eliminate fall hazards around bench seating.
Perimeter bench seating was installed at one or more decks where walking surfaces were more than 30 inches above the surrounding grade. Bench seating is not a safe substitute for standard guardrails, and is a potential fall hazard. Gaps in such seating often allow small children to climb underneath and fall. People sitting or standing on benches may also fall. The clients should at least be aware of this hazard, especially if small children are present. Recommend having a qualified contractor repair as necessary to eliminate fall hazards around bench seating.
5) 
 Significant rot, deterioration, leaning and/or bowing were found in one or more timber retaining walls. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair or replace sections as necessary.
Significant rot, deterioration, leaning and/or bowing were found in one or more timber retaining walls. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair or replace sections as necessary.
Crawl Space
8) 
 Fungal rot was found at one or more rim joist areas, however no elevated moisture readings were found at these areas at the time of the inspection. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary. In some cases it may be possible to repair with an epoxy penetrant and filler which can be found at most hardware stores. For more information visit:
Fungal rot was found at one or more rim joist areas, however no elevated moisture readings were found at these areas at the time of the inspection. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary. In some cases it may be possible to repair with an epoxy penetrant and filler which can be found at most hardware stores. For more information visit:
http://www.oldhousefix.com/fixing-decayed-rotted-wood/
http://www.oldhousefix.com/fixing-decayed-rotted-wood/
9) 
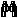 Minor amounts of standing water as well as evidence of substantial prior water intrusion (stains on foam board, rust on support posts, etc) was found at one or more locations in the crawl space. Some minor seasonal water accumulation can be normal. However significant amounts of water may evaporate and enter the structure above causing high levels of moisture in the structure. This can be a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Rain runoff is the most common cause of wet crawl spaces but water can come from other sources such as groundwater or underground springs. Recommend monitoring the crawl space in the future, especially after heavy and/or prolonged periods of rain. Correct any issues related to outside perimeter grading and/or roof drainage (see any other comments about this in this report). Also, review any disclosure statements available and ask the property owner about past accumulation of water in the crawl space.
Minor amounts of standing water as well as evidence of substantial prior water intrusion (stains on foam board, rust on support posts, etc) was found at one or more locations in the crawl space. Some minor seasonal water accumulation can be normal. However significant amounts of water may evaporate and enter the structure above causing high levels of moisture in the structure. This can be a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Rain runoff is the most common cause of wet crawl spaces but water can come from other sources such as groundwater or underground springs. Recommend monitoring the crawl space in the future, especially after heavy and/or prolonged periods of rain. Correct any issues related to outside perimeter grading and/or roof drainage (see any other comments about this in this report). Also, review any disclosure statements available and ask the property owner about past accumulation of water in the crawl space.
If standing water persists or increases in amount, recommend that a qualified contractor who specializes in drainage issues evaluate and repair as necessary. Typically such repairs include:
If standing water persists or increases in amount, recommend that a qualified contractor who specializes in drainage issues evaluate and repair as necessary. Typically such repairs include:
- Repairing, installing or improving underground footing and/or curtain drains
- Applying waterproof coatings to foundation walls
- Digging trenches in the crawl space to collect or divert water
- Crawl space encapsulation
- Installing sump pumps
10)  No vapor barrier was installed in the crawl space. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms due to the likelihood of water evaporating from the soil below up into the structure. A 6 mil black plastic sheet should be placed over all exposed soil with seams overlapped to 24 inches, and not in contact with any wood structural components. The sheeting should be held in place with bricks or stones, not wood. Recommend that a qualified contractor install a vapor barrier per standard building practices.
No vapor barrier was installed in the crawl space. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms due to the likelihood of water evaporating from the soil below up into the structure. A 6 mil black plastic sheet should be placed over all exposed soil with seams overlapped to 24 inches, and not in contact with any wood structural components. The sheeting should be held in place with bricks or stones, not wood. Recommend that a qualified contractor install a vapor barrier per standard building practices.
Roof
12)  The starter strip at the garage roof was deteriorated at some eave areas. This can lead to rot at sheathing edges. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
The starter strip at the garage roof was deteriorated at some eave areas. This can lead to rot at sheathing edges. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
13)  Significant amounts of debris have accumulated in one or more gutters or downspouts. Gutters can overflow and cause water to come in contact with the building exterior, or water can accumulate around the foundation. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend cleaning gutters and downspouts now and as necessary in the future.
Significant amounts of debris have accumulated in one or more gutters or downspouts. Gutters can overflow and cause water to come in contact with the building exterior, or water can accumulate around the foundation. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend cleaning gutters and downspouts now and as necessary in the future.
14)  Moss was growing on the roof in some areas. As a result, shingles can lift or be damaged. Leaks can result and/or the roof surface can fail prematurely. Efforts should be made to kill the moss during its growing season (wet months). Typically, zinc or phosphate-based chemicals are used for this and must be applied periodically. For information on various moss treatment products and their pros and cons, visit:
Moss was growing on the roof in some areas. As a result, shingles can lift or be damaged. Leaks can result and/or the roof surface can fail prematurely. Efforts should be made to kill the moss during its growing season (wet months). Typically, zinc or phosphate-based chemicals are used for this and must be applied periodically. For information on various moss treatment products and their pros and cons, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?MOSS
http://www.reporthost.com/?MOSS
Garage or Carport
17) 

 The auto-reverse mechanism on both of the automatic openers for the garage vehicle doors was inoperable. This is a potential safety hazard. The auto reverse is a back-up safety feature (it operates independently from the sensors on the door rails) that raises the door if it comes in contact with an object. A qualified contractor should evaluate and repair as necessary. For more information on garage door safety issues, visit:
The auto-reverse mechanism on both of the automatic openers for the garage vehicle doors was inoperable. This is a potential safety hazard. The auto reverse is a back-up safety feature (it operates independently from the sensors on the door rails) that raises the door if it comes in contact with an object. A qualified contractor should evaluate and repair as necessary. For more information on garage door safety issues, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?NRGD
http://www.reporthost.com/?NRGD
18)  Rusted areas were seen at both of the garage vehicle doors. Recommend repair or replacement. The rusted areas can sometimes be repaired by applying an auto-body putty filler, sanding and painting with a rust inhibitive paint. For information go to:
Rusted areas were seen at both of the garage vehicle doors. Recommend repair or replacement. The rusted areas can sometimes be repaired by applying an auto-body putty filler, sanding and painting with a rust inhibitive paint. For information go to:
https://homeguides.sfgate.com/restore-rusted-metal-door-46121.html
https://homeguides.sfgate.com/restore-rusted-metal-door-46121.html
19)  Vegetation was in contact with or close to the building exterior. Vegetation can serve as a pathway for wood-destroying insects and can retain moisture against the exterior after it rains. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend pruning, moving or removing vegetation as necessary to maintain at least 6 inches of space between it and the building exterior. A 1-foot clearance is better.
Vegetation was in contact with or close to the building exterior. Vegetation can serve as a pathway for wood-destroying insects and can retain moisture against the exterior after it rains. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend pruning, moving or removing vegetation as necessary to maintain at least 6 inches of space between it and the building exterior. A 1-foot clearance is better.
20) 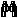 Stains were found in one or more ceiling areas. However, no elevated levels of moisture were found at the time of the inspection. The stain appears to be be due to past roof leaks. Monitor the stained area in the future, especially after heavy or prolonged rain. If elevated moisture is found in the future, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary.
Stains were found in one or more ceiling areas. However, no elevated levels of moisture were found at the time of the inspection. The stain appears to be be due to past roof leaks. Monitor the stained area in the future, especially after heavy or prolonged rain. If elevated moisture is found in the future, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary.
Electric
25) 

 One or more electric receptacles at the garage, exterior and shed had no ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection. If not GFCI-protected, receptacles in wet areas pose a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install GFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for GFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
One or more electric receptacles at the garage, exterior and shed had no ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection. If not GFCI-protected, receptacles in wet areas pose a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install GFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for GFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
http://www.reporthost.com/?GFCI
- Outdoors (since 1973)
- Bathrooms (since 1975)
- Garages (since 1978)
- Kitchens (since 1987)
- Crawl spaces and unfinished basements (since 1990)
- Wet bar sinks (since 1993)
- Laundry and utility sinks (since 2005)
http://www.reporthost.com/?GFCI
26) 
 Bare wire ends, or wires with a substandard termination, were found at one or more locations. This is a potential shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For example, by cutting wires to length and terminating with wire nuts in a permanently mounted, covered junction box.
Bare wire ends, or wires with a substandard termination, were found at one or more locations. This is a potential shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For example, by cutting wires to length and terminating with wire nuts in a permanently mounted, covered junction box.
Larger shed
Larger shed
27) 
 One or more electric receptacles had reverse-polarity wiring, where the hot and neutral wires were reversed. This is a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
One or more electric receptacles had reverse-polarity wiring, where the hot and neutral wires were reversed. This is a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?RPR
http://www.reporthost.com/?RPR
28) 
 One or more smoke alarms were missing, damaged, or missing components. Smoke alarms should be replaced as necessary. For more information, visit:
One or more smoke alarms were missing, damaged, or missing components. Smoke alarms should be replaced as necessary. For more information, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
http://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
29) 
 One or more cover plates for switches, receptacles or junction boxes were missing or broken. These plates are intended to contain fire and prevent electric shock from occurring due to exposed wires. Recommend that a qualified person install cover plates where necessary.
One or more cover plates for switches, receptacles or junction boxes were missing or broken. These plates are intended to contain fire and prevent electric shock from occurring due to exposed wires. Recommend that a qualified person install cover plates where necessary.
30)  One or more covers for light fixtures were missing. Recommend replacing as necessary to avoid exposed bulbs.
One or more covers for light fixtures were missing. Recommend replacing as necessary to avoid exposed bulbs.
31)  One garage light fixture was loose. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary.
One garage light fixture was loose. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary.
Plumbing / Fuel Systems
32) 
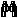 Sand was found at the bottom of the pit liner for the sump pump. This can be an indication of failing drain tile and can clog and damage the pump. Recommend cleaning liner and drain tile ends and monitoring in the future.
Sand was found at the bottom of the pit liner for the sump pump. This can be an indication of failing drain tile and can clog and damage the pump. Recommend cleaning liner and drain tile ends and monitoring in the future.
33)  The hose bib leaked when tested. When hose bibs leak while turned off, it's often caused by a worn valve seat or a loose bonnet. When hose bibs leak while turned on, it may be due to worn "packing" around the stem or a defective backflow prevention device. Recommend that a qualified plumber repair as necessary.
The hose bib leaked when tested. When hose bibs leak while turned off, it's often caused by a worn valve seat or a loose bonnet. When hose bibs leak while turned on, it may be due to worn "packing" around the stem or a defective backflow prevention device. Recommend that a qualified plumber repair as necessary.
Private Well
34)  Because this is a specialty system, recommend the following:
Because this is a specialty system, recommend the following:
http://www.reporthost.com/?WELL
- That a qualified well contractor fully evaluate the well, including a pump/flow test
- That the well water be tested per the client's concerns (e.g. coliforms, pH, contaminants) by a qualified lab
- That the client research the well's history (e.g. how/when constructed, how/when maintained or repaired, past performance, past health issues)
- That that the client document the current well capacity and water quality for future reference
http://www.reporthost.com/?WELL
Heating, Ventilation and Air Condition (HVAC)
35) 
 Corrosion or rust was found in the fitting for the circulating pump. This can indicate past leaks, or that leaks are likely to occur in the future. Recommend that a qualified heating contractor or plumber evaluate and repair as necessary.
Corrosion or rust was found in the fitting for the circulating pump. This can indicate past leaks, or that leaks are likely to occur in the future. Recommend that a qualified heating contractor or plumber evaluate and repair as necessary.
36)  An automatic air bleed valve had leaked and the cap was screwed completely down to prevent further leakage. Automatic air bleeders, to work, require that their screw cap (it looks like a tire valve stem cap) be left loose so that the float inside the automatic air purger/bleeder can release air when needed. This valve is defective and should be repaired or replaced.
An automatic air bleed valve had leaked and the cap was screwed completely down to prevent further leakage. Automatic air bleeders, to work, require that their screw cap (it looks like a tire valve stem cap) be left loose so that the float inside the automatic air purger/bleeder can release air when needed. This valve is defective and should be repaired or replaced.
Kitchen
37)  The digital display on the range was unreadable. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
The digital display on the range was unreadable. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
38)  Water was leaking at the sink faucet base. Recommend that a qualified plumber repair as necessary.
Water was leaking at the sink faucet base. Recommend that a qualified plumber repair as necessary.
Bathrooms, Laundry and Sinks
39)  The sink faucet at location #A was dripping when off. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
The sink faucet at location #A was dripping when off. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
Interior, Doors and Windows
40) 
 One or more screen doors were difficult to open or close. Recommend that a qualified person evaluate and repair or replace as necessary.
One or more screen doors were difficult to open or close. Recommend that a qualified person evaluate and repair or replace as necessary.
Sliding screen door
Sliding screen door
41) 
 Condensation or staining was visible between multi-pane glass in one or more windows. This usually indicates that the seal between the panes of glass has failed or that the desiccant material that absorbs moisture is saturated. As a result, the view through the window may be obscured, the window's R-value will be reduced, and accumulated condensation may leak into the wall structure below. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair windows as necessary. Usually, this means replacing the glass in window frames.
Condensation or staining was visible between multi-pane glass in one or more windows. This usually indicates that the seal between the panes of glass has failed or that the desiccant material that absorbs moisture is saturated. As a result, the view through the window may be obscured, the window's R-value will be reduced, and accumulated condensation may leak into the wall structure below. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair windows as necessary. Usually, this means replacing the glass in window frames.
Be aware that evidence of failed seals or desiccant may be more or less visible depending on the temperature, humidity, sunlight, etc. Windows or glass-paneled doors other than those that the inspector identified may also have failed seals and need glass replaced. It is beyond the scope of this inspection to identify every window with failed seals or desiccant.
Be aware that evidence of failed seals or desiccant may be more or less visible depending on the temperature, humidity, sunlight, etc. Windows or glass-paneled doors other than those that the inspector identified may also have failed seals and need glass replaced. It is beyond the scope of this inspection to identify every window with failed seals or desiccant.
42)  Carpeting in one or more areas was damaged. Recommend that a qualified contractor replace as necessary.
Carpeting in one or more areas was damaged. Recommend that a qualified contractor replace as necessary.
43)  One or more bifold doors were off their track(s) or difficult to operate. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
One or more bifold doors were off their track(s) or difficult to operate. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
44)  The floor sweep at the front door was damaged. Recommend that a qualified person repair or replace as necessary.
The floor sweep at the front door was damaged. Recommend that a qualified person repair or replace as necessary.
45)  One or more skylight wells (the inside structure around skylights) was damaged, possibly by past condensation or water leaks. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
One or more skylight wells (the inside structure around skylights) was damaged, possibly by past condensation or water leaks. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
46)  Tile, stone and/or grout in the flooring in one or more areas was deteriorated (e.g. loose or cracked tiles, missing grout) or substandard. If in a wet area, water can damage the sub-floor. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
Tile, stone and/or grout in the flooring in one or more areas was deteriorated (e.g. loose or cracked tiles, missing grout) or substandard. If in a wet area, water can damage the sub-floor. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
47) 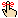 Minor cracks, nail pops and/or blemishes were found in walls and/or ceilings in one or more areas. Cracks and nail pops are common, are often caused by lumber shrinkage or minor settlement, and can be more or less noticeable depending on changes in humidity. They did not appear to be a structural concern, but the client may wish to repair these for aesthetic reasons. For recurring cracks, consider using an elastic crack covering product:
Minor cracks, nail pops and/or blemishes were found in walls and/or ceilings in one or more areas. Cracks and nail pops are common, are often caused by lumber shrinkage or minor settlement, and can be more or less noticeable depending on changes in humidity. They did not appear to be a structural concern, but the client may wish to repair these for aesthetic reasons. For recurring cracks, consider using an elastic crack covering product:
http://www.reporthost.com/?ECC
http://www.reporthost.com/?ECC
48)  Carpeting in one or more areas was significantly stained or soiled. Recommend having carpeting professionally cleaned as necessary.
Carpeting in one or more areas was significantly stained or soiled. Recommend having carpeting professionally cleaned as necessary.
49) 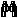 Stains were found in one or more ceiling areas. However, no elevated levels of moisture were foundat the time of the inspection. The stain(s) may be due to past roof leas. Monitor the stained area(s) in the future, especially after heavy or prolonged rain. If elevated moisture is found in the future, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary.
Stains were found in one or more ceiling areas. However, no elevated levels of moisture were foundat the time of the inspection. The stain(s) may be due to past roof leas. Monitor the stained area(s) in the future, especially after heavy or prolonged rain. If elevated moisture is found in the future, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary.
Outbuildings and Sheds
51)  Some composition shingles were damaged or missing. Leaks can occur as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary. For example, by replacing shingles.
Some composition shingles were damaged or missing. Leaks can occur as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary. For example, by replacing shingles.
52)  Fungal rot was found at one or more sections of siding or trim. Conducive conditions for rot should be corrected (e.g. wood-soil contact, reverse perimeter slope). Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary. Rotten wood should be replaced or repaired with an epoxy penetrant and filler which can be found at most hardware stores. For more information visit:
Fungal rot was found at one or more sections of siding or trim. Conducive conditions for rot should be corrected (e.g. wood-soil contact, reverse perimeter slope). Recommend that a qualified contractor repair as necessary. Rotten wood should be replaced or repaired with an epoxy penetrant and filler which can be found at most hardware stores. For more information visit:
http://www.oldhousefix.com/fixing-decayed-rotted-wood/
http://www.oldhousefix.com/fixing-decayed-rotted-wood/
53)  The roof structure over the bathroom area on the large shed was damaged or deteriorated. Recommend a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
The roof structure over the bathroom area on the large shed was damaged or deteriorated. Recommend a qualified contractor repair as necessary.
54)  Moss was growing on shed roofs. As a result, shingles can lift or be damaged. Leaks can result and/or the roof surface can fail prematurely. Efforts should be made to kill the moss during its growing season (wet months). Typically, zinc or phosphate-based chemicals are used for this and must be applied periodically. For information on various moss treatment products and their pros and cons, visit:
Moss was growing on shed roofs. As a result, shingles can lift or be damaged. Leaks can result and/or the roof surface can fail prematurely. Efforts should be made to kill the moss during its growing season (wet months). Typically, zinc or phosphate-based chemicals are used for this and must be applied periodically. For information on various moss treatment products and their pros and cons, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?MOSS
http://www.reporthost.com/?MOSS
55)  Vegetation was in contact with or close to the building exterior. Vegetation can serve as a pathway for wood-destroying insects and can retain moisture against the exterior after it rains. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend pruning, moving or removing vegetation as necessary to maintain at least 6 inches of space between it and the building exterior. A 1-foot clearance is better.
Vegetation was in contact with or close to the building exterior. Vegetation can serve as a pathway for wood-destroying insects and can retain moisture against the exterior after it rains. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend pruning, moving or removing vegetation as necessary to maintain at least 6 inches of space between it and the building exterior. A 1-foot clearance is better.
